Scaling tests on Google Kubernetes Engine with Cloud Build
A guide to running test automation scripts in distributed env using gitops approach
As we looked at how to run automation scripts in selenoid using docker and docker-compose in my previous blog. In this blog let’s dive into how to run WebdriverIO test automation scripts in scalable mode using Google Kubernetes Engine and Cloud Build.
Kubernetes is an open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications. Google Kubernetes Engine — provides a simple way to automatically deploy, scale, and manage Kubernetes. And Cloud Build — it is a serverless CI/CD platform to build, test, and deploy.
According to the documentation of Aerokube, selenoid is not recommended for the Kubernetes platform. And Moon is pay per use model. So in this article, we are going to explore Selenosis — a scalable, stateless selenium hub for the Kubernetes cluster.
Selenosis setup walkthrough
1. Creating a namespace
Namespaces are Kubernetes objects which help in organising resources and partition a single Kubernetes cluster into multiple virtual clusters. It provides a degree of isolation from the other parts of the cluster.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: selenosis
2. Creating service for selenosis
Service is an abstract way to expose an application running on a set of Pods as a network service. It creates a permanent IP address, the lifecycle of pod and service are not connected. Even if the pods crash and are recreated, the service IP remains the same.
3. Creating selenosis deployment
Deployment describes the desired state of a pod or a replica set, then gradually updates the environment (for example, creating or deleting replicas) until the current state matches the desired state specified in the deployment file. In general, we don’t work directly with pods, we will create deployments. It is mainly for stateless apps.
4. Selenosis HPA
Horizontal Pod Autoscaler automatically scales the number of Pods in a replication controller, deployment, replica set or stateful set based on observed CPU utilisation
5. Other configs
-
Below is the command to convert the browser yaml file into ConfigMap
kubectl create cm selenosis-config --from-file=browsers.yaml=selenosis-deploy/browsers.yaml -n selenosis
-
Use core-dns.yaml to turn off the DNS caching for the selenosis namespace
-
Use pre-pull-image.yaml to pre pull the chrome and firefox browser images
-
To debug use selenoid-ui.yaml ***which enables the UI feature to debug
Containerizing test scripts
Jobs used to run a finite task(which is a suitable k8s object to use for running test scripts). It will create one or more Pods and performs a given task. Once the task is completed successfully, the pod will be exited.
Creating a project in GCP
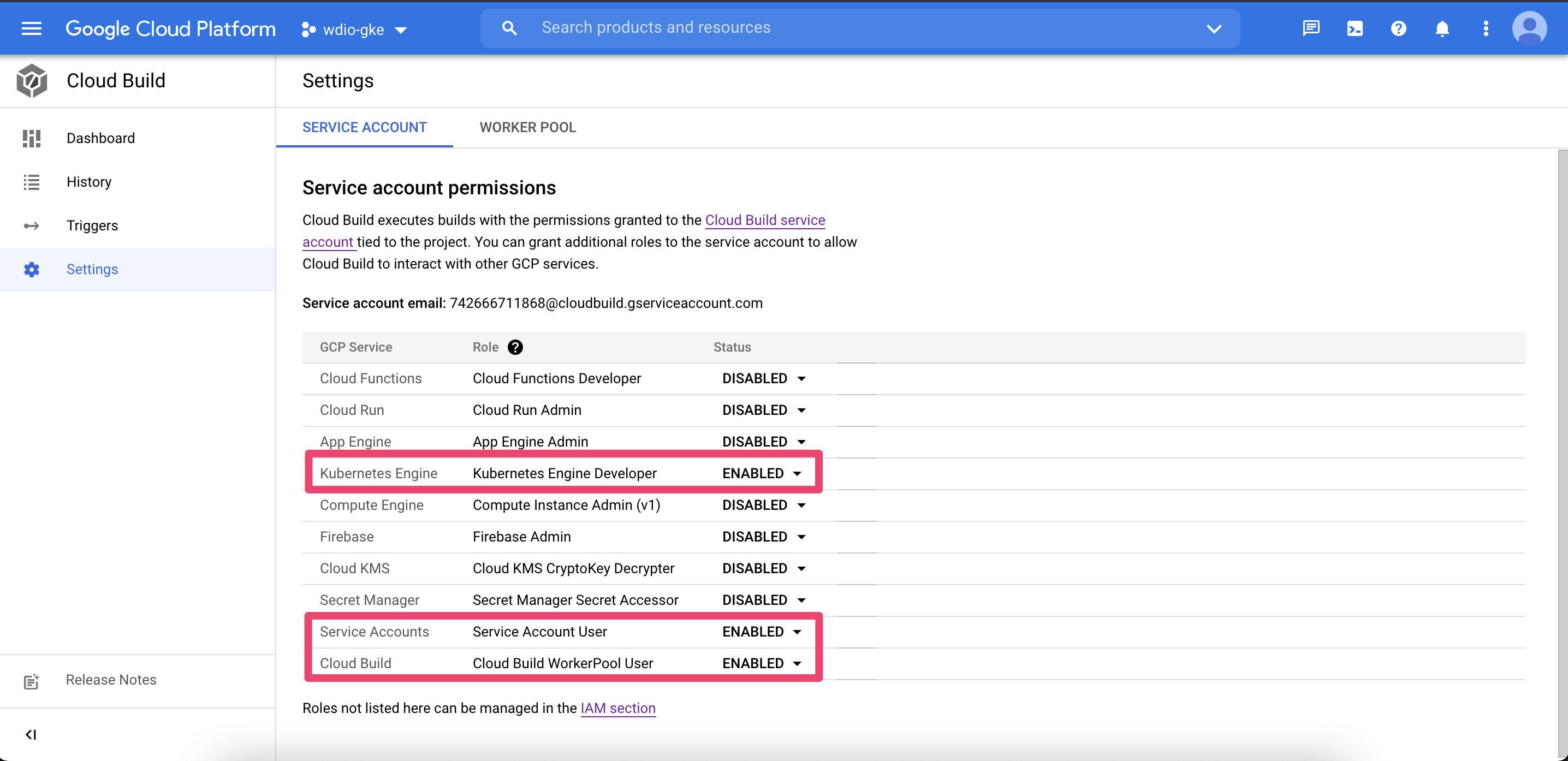
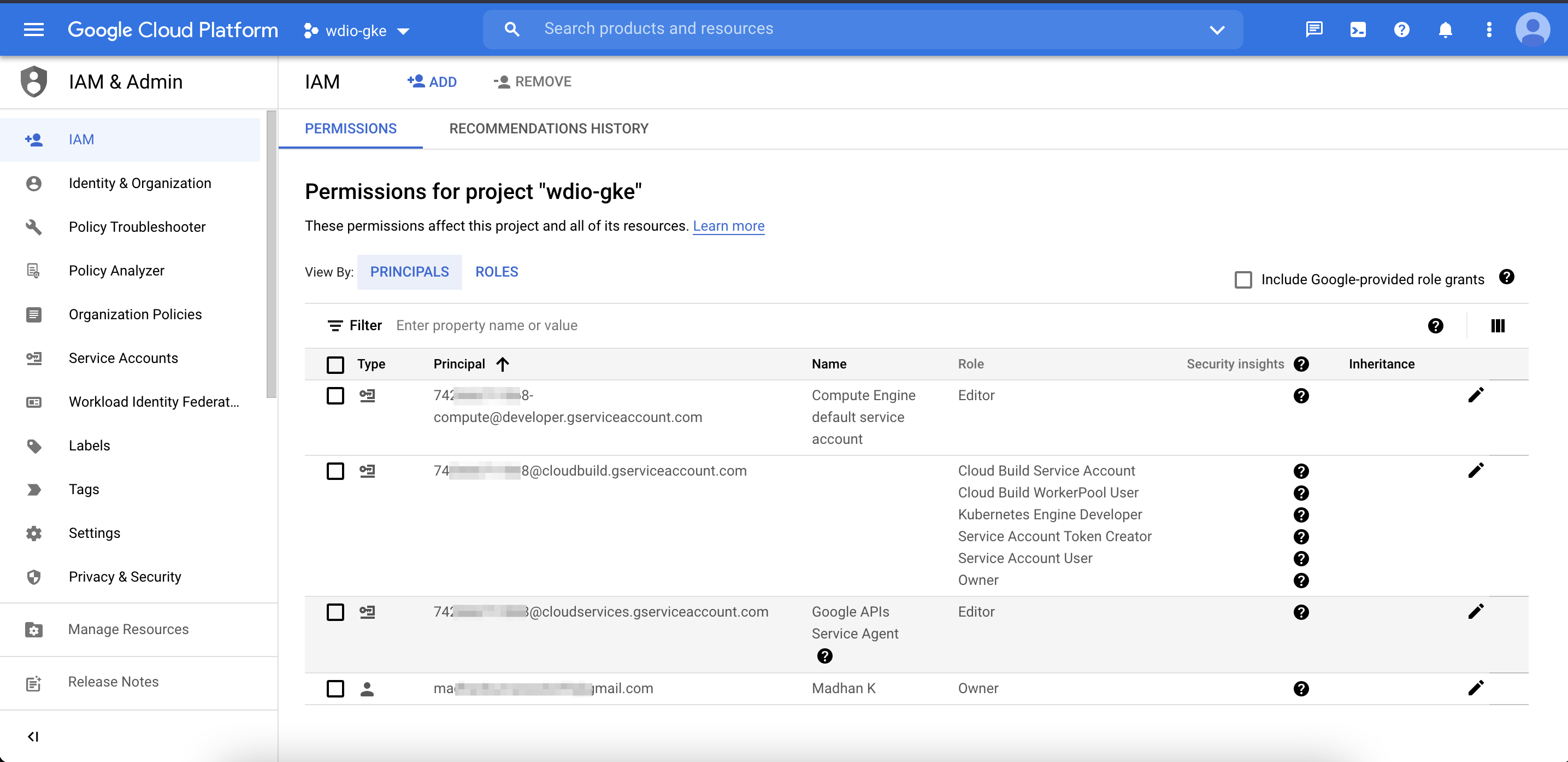
Create a new project in GCP, go to Cloud Build, enable the api. And few other settings as shown in the below picture (to follow along with this tutorial you need a cloud billing account, a *free tier* is sufficient). And make sure you have the required permissions in the IAM & Admin section.
Setting up Cloud build
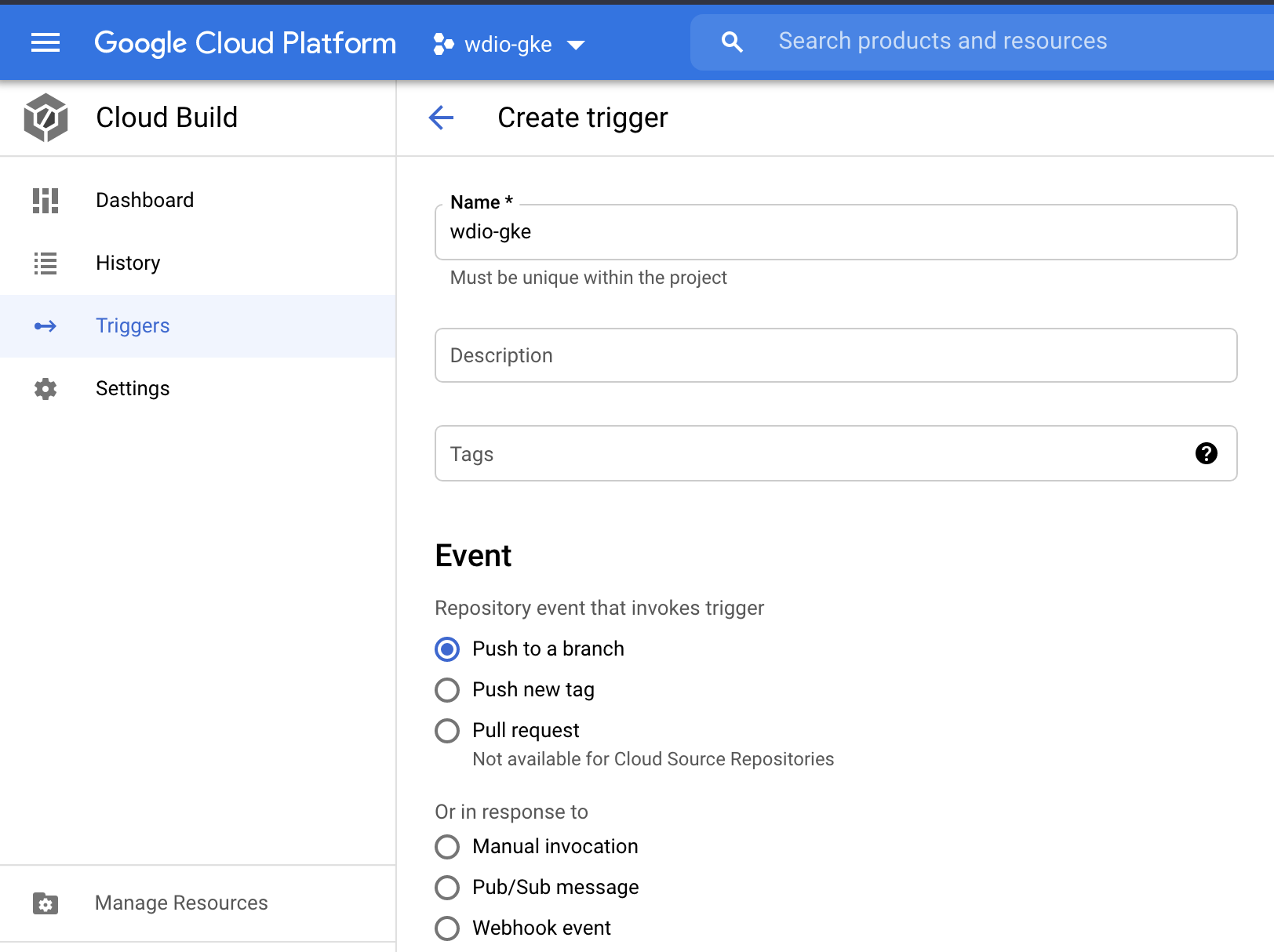
Go to Cloud Build > Triggers section, click on Create Trigger and add the details as follow. So whenever the code has been pushed to GitHub, cloud build flow will be triggered.
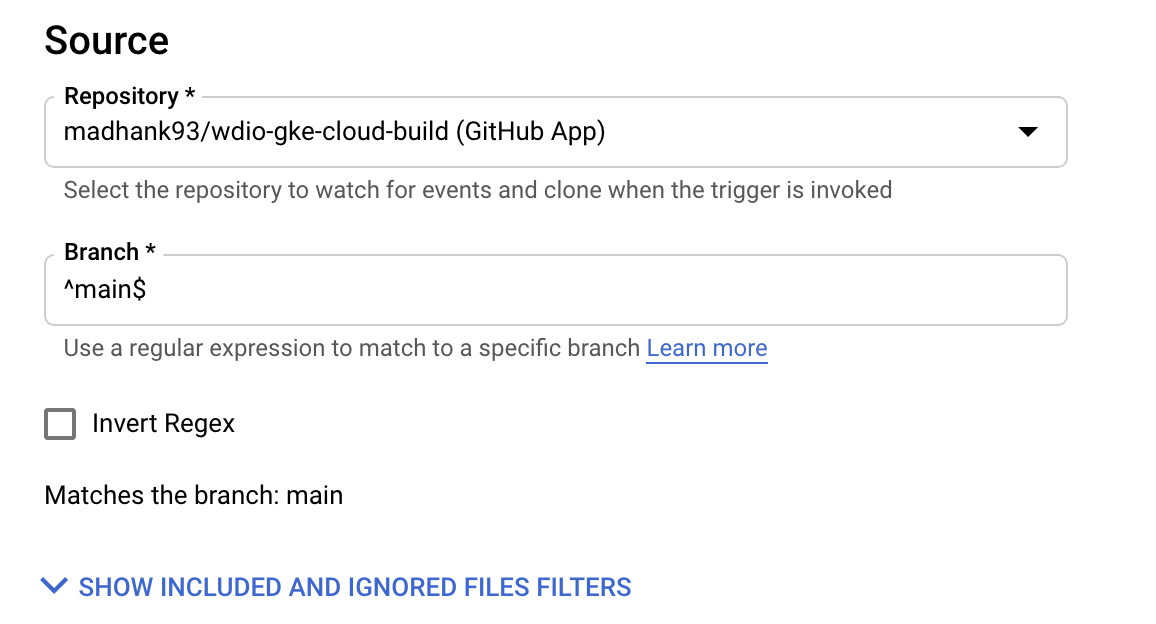
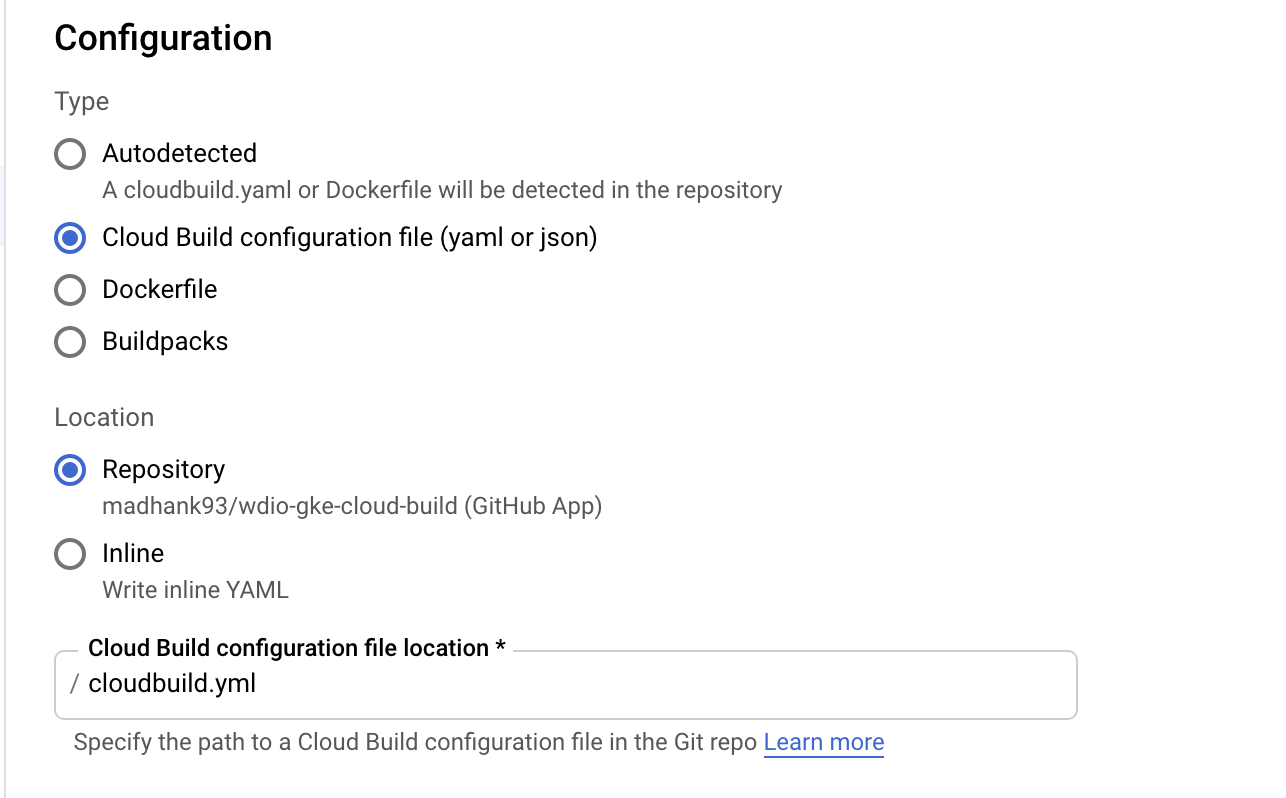
And finally creating cloudbuild.yml file to execute the process of building docker image from source code (e2e), pushing it to a container registry, creating a GKE cluster and finally starting e2e tests.
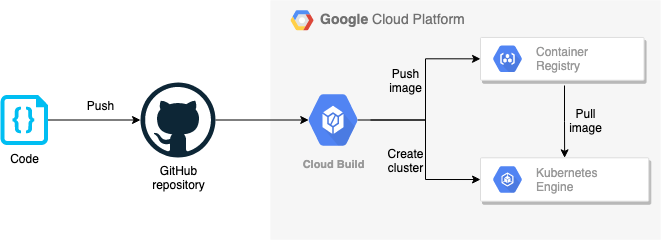
Execution
According to the cloud build settings, whenever the code has been pushed to Github repositories, execution will begin.
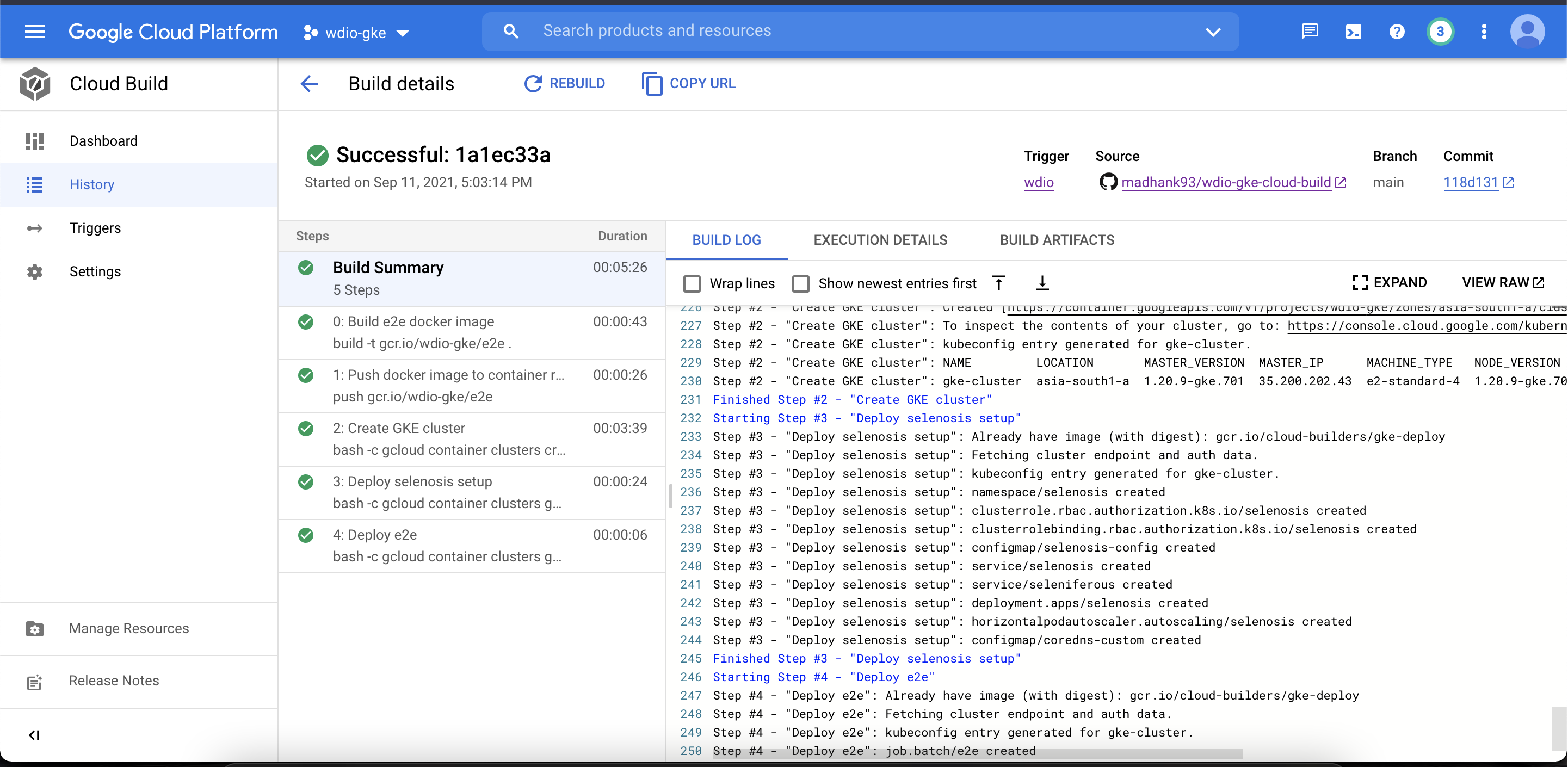
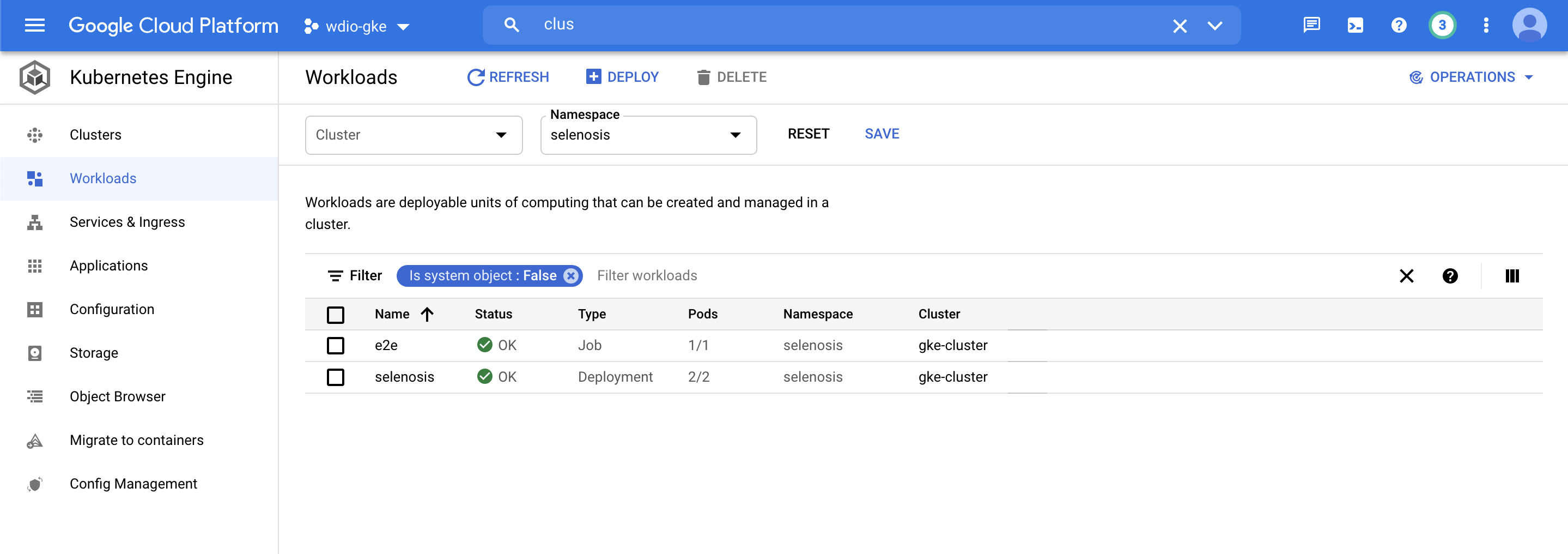
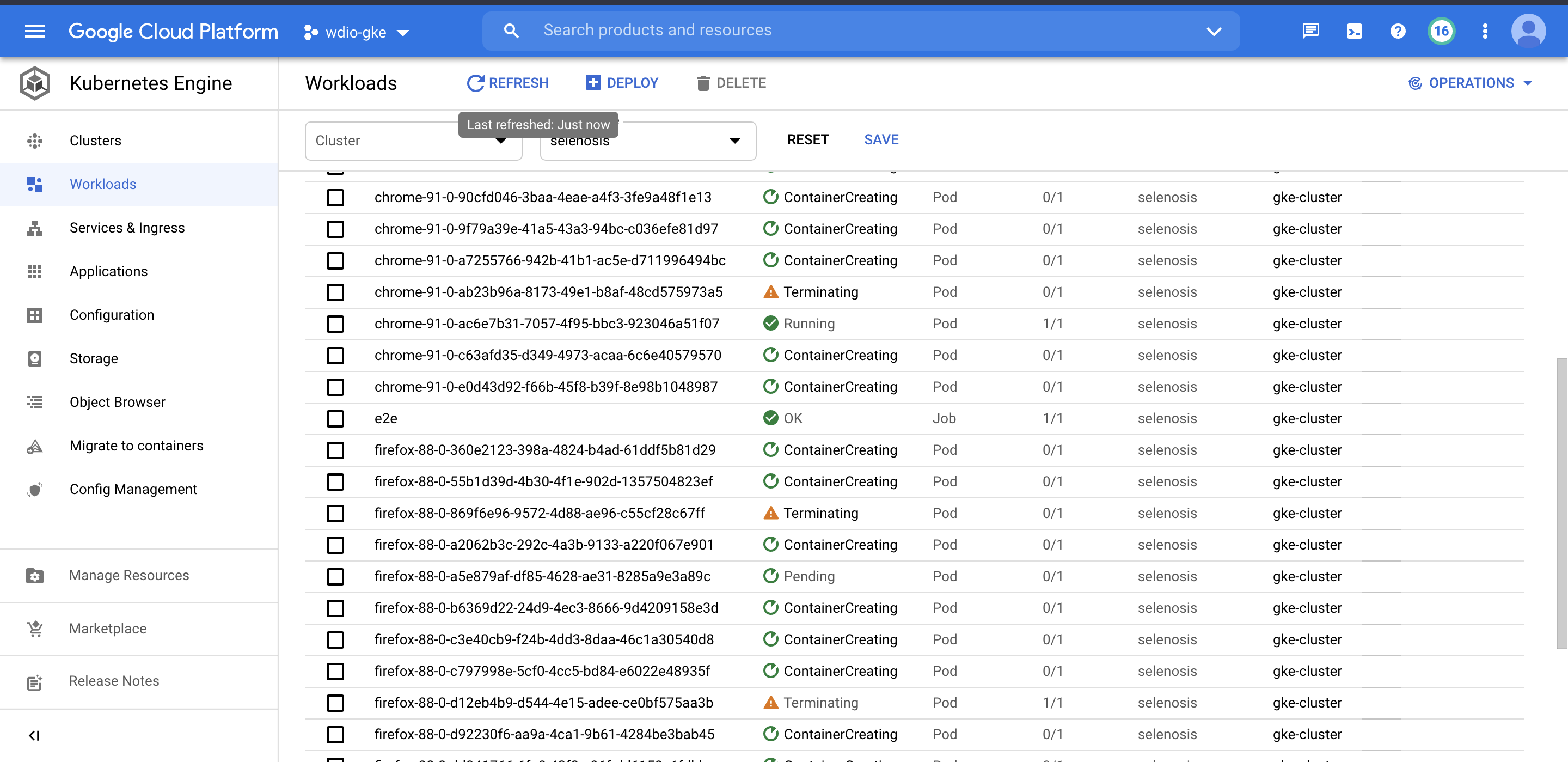
Result
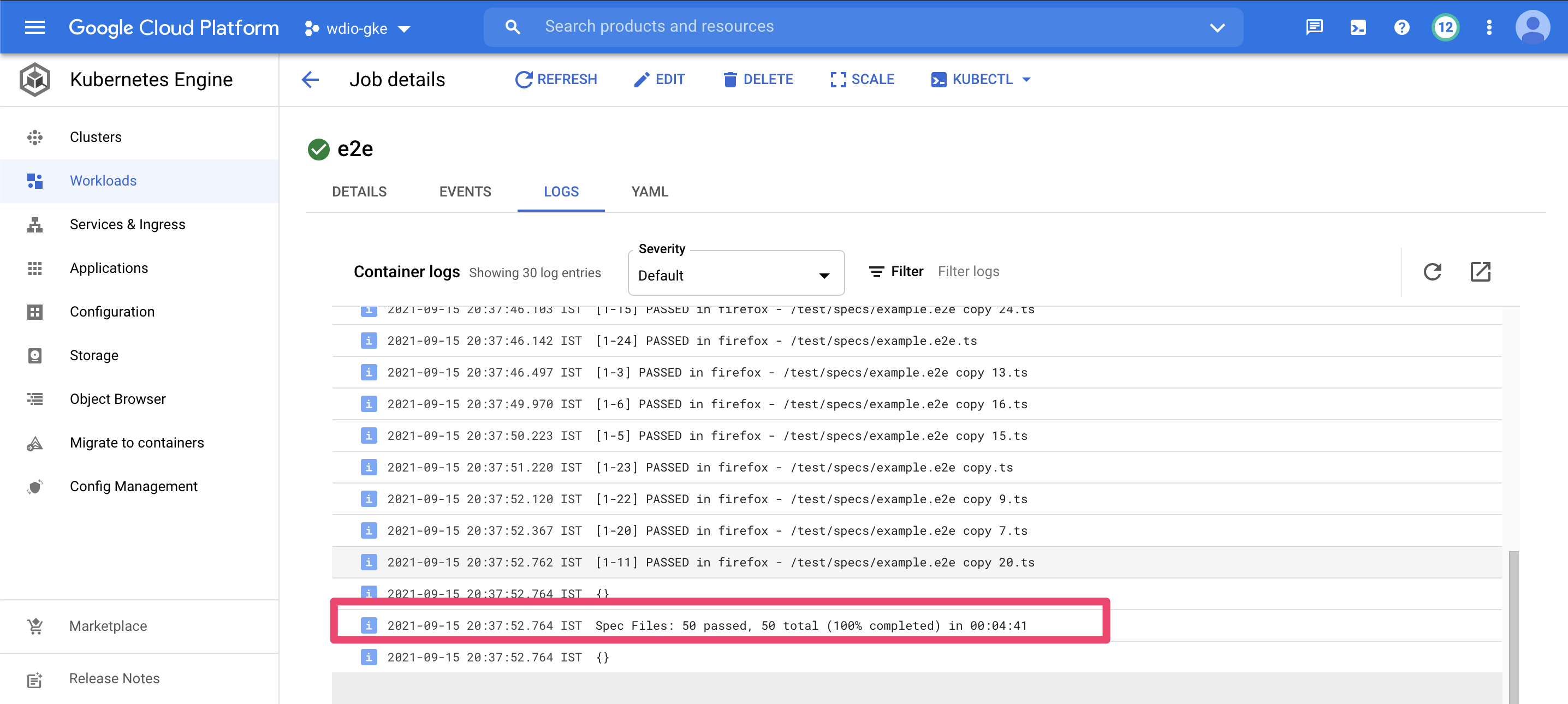
Running all the 25 spec/tests files in chrome and firefox browsers parallelly, and completing it all within well under 04:41 mins. More or less time remains constant since all the tests are running in parallel no matter how many tests scripts has been authored, maximum time will take to complete the whole process will the slowest of all the test.
⚠️❗⚠️ Finally make sure to delete the GKE cluster and Container images to avoid any charges.
Originally published on Medium
🌟 🌟 🌟 The source code for this blog post can be found here 🌟🌟🌟
References:
[1] https://github.com/alcounit/selenosis
[2] https://github.com/alcounit/selenosis-deploy
[3] https://cloud.google.com/kubernetes-engine/docs/tutorials/gitops-cloud-build
[4] https://codefresh.io/kubernetes-tutorial/single-use-daemonset-pattern-pre-pulling-images-kubernetes/