Simplifying Bank statement analysis using Marker and Ollama
A guide to using Streamlit, Marker, Ollama and the Phi-4 model for seamless data extraction

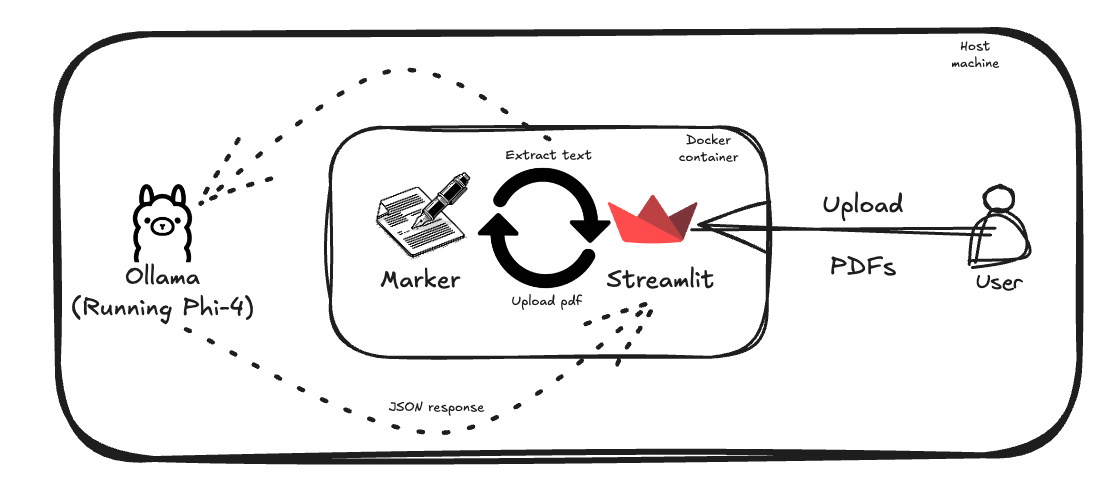
In this article we will take look into a project designed to simplify bank statement analysis. By combining a Streamlit based interface, Marker’s PDF text extraction capabilities, and the Phi-4 model from Microsoft using Ollama, the system efficiently extracts and processes transaction data from uploaded PDFs.
The workflow is straightforward:
-
Upload bank statement PDFs via a Streamlit app.
-
Use Marker to extract text from the PDFs.
-
Process the extracted text through the Phi-4 model running on Ollama to convert it into a structured JSON schema.
Setup:
Since I am using a MacBook, Ollama is installed natively on the host machine. This approach avoids limitations posed by Docker’s lack of GPU support for containers. To set up the Phi-4 model, use the following command:
ollama run phi4
Other components, like Streamlit and Marker, are set up easily using development containers; install the dev containers plugin in VS code and use the Open folder in Container option. I used Orbstack to manage Docker containers.
i) Extracting text from PDFs:
Marker simplifies the process of extracting text from uploaded PDF files. It also supports output formats such as Markdown, HTML, and JSON. Below is a Python function leveraging Marker to extract text.
def extract_pdf_text(pdf_files: List) -> str:
"""Extract text from uploaded PDF files using Marker"""
text = ""
converter = PdfConverter(artifact_dict=create_model_dict(),)
for uploaded_file in pdf_files:
with open("temp.pdf", "wb") as f:
f.write(uploaded_file.getvalue())
rendered = converter("temp.pdf")
extracted_text, _, _ = text_from_rendered(rendered)
text += extracted_text
os.remove("temp.pdf")
return text
ii) Converting the raw text into a JSON schema:
Ollama supports structured JSON output. Using the Pydantic library, we can define a schema to represent account holder details and transaction data.
class AccountHolder(BaseModel):
name: str
account_number: str
class Transaction(BaseModel):
date: str
amount: float
currency: str
type: str
description: str
balance: float
class BankStatement(BaseModel):
account_holder: AccountHolder
transactions: List[Transaction]
To process the extracted text, the Phi-4 model is queried via an API call. The schema is passed as a parameter, making the output highly structured and usable.
def process_bank_transactions(text: str) -> json:
"""Process text through Ollama phi4 model"""
ollama_host = os.getenv('OLLAMA_HOST', 'host.docker.internal')
url = f"http://{ollama_host}:11434/api/chat"
payload = {
"model": "phi4",
"messages": [
{
"role": "system",
"content": f"{SYSTEM_MESSAGE}"
},
{
"role": "user",
"content": f"{text}"
}
],
"format": BankStatement.model_json_schema(),
"stream": False
}
try:
response = requests.post(url, json=payload, timeout=300)
response.raise_for_status()
response_data = response.json()
if 'message' in response_data:
try:
content = response_data['message']['content']
transactions = json.loads(content)
return {"data": transactions}
except json.JSONDecodeError:
return {"error": "Failed to parse model response as JSON"}
else:
return {"error": "Unexpected response format from model"}
except requests.exceptions.Timeout:
return {"error": "Request timed out connecting to Ollama"}
except requests.exceptions.ConnectionError:
return {"error": "Failed to connect to Ollama server"}
except Exception as e:
return {"error": f"Unexpected error: {str(e)}"}
Results and Accuracy
The system achieves an accuracy of approximately 80% when converting transaction text into structured JSON. This can be further improved by refining the input prompts and tailoring the schema definitions to specific bank statement formats.
Originally published on Medium
🌟 🌟 🌟 The source code for this blog post can be found here 🌟🌟🌟
Reference:
[1] https://github.com/VikParuchuri/marker
[2] https://docs.pydantic.dev/latest/concepts/models/